Photovoltaic (PV) systems are used to convert sunlight into electricity.
The installation of PV systems on both low-slope and steep-slope roofs has increased due to an increase in energy awareness and government incentives.
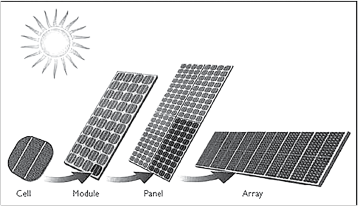
A PV module/panel consists of many PV cells, and a combination of PV modules makes up a PV array. Photovoltaic systems consist of PV panels and their associated electrical components (inverters, disconnects and wiring). PV cells convert the energy of light into direct current (DC) electricity.
Rack-mounted systems are the most common mounting configuration for PV systems. These PV systems consist of PV arrays that are arranged on frames or structures referred to as “racks”. The methods that rack mounted PV systems are installed on the rooftop are:
- Direct connection
- Ballast
- Hybrid
Direct Connection
Direct connection involves multiple penetrations and connections to the structural framing of the roof. These penetrations require proper tie-in and flashing into the roofing system.
Ballast
The second method involves the use of ballast to secure the panels. The weights of the array, racking system and additional ballast material are used to prevent wind uplift and displacement. The advantage of this method is that fewer roof penetrations have to be made watertight.
Hybrid
The hybrid method consists of a limited number of structural connections through the roof combined with ballast material. Where this method is used, the general rule of thumb is that the fewer the number of connections, the more ballast required and vice-versa.
